Organisation name: Clinical Research Excellence Foundation (formerly known as ClinverseEdge)

27 January, 2026
Author : Dr Vijaykumar Gawali
Topic : COLLECTION, STORAGE & PROCESSING OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES
1 Definition
Biological samples include blood, urine, saliva, biopsies, or other human specimens collected for laboratory analysis.
Handling samples requires strict adherence to:
- Protocol
- Laboratory Manual
- IATA guidelines (for shipment)
- Site SOPs
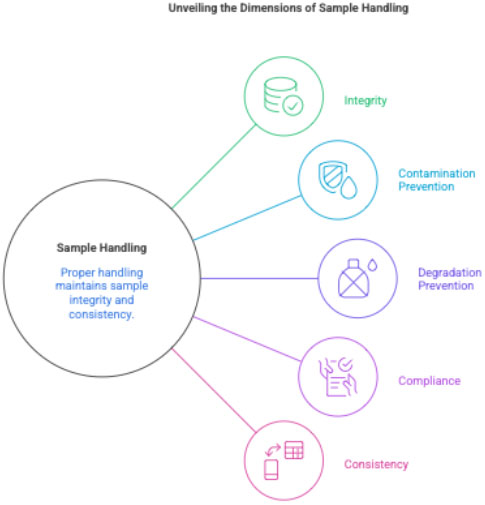
2 Purpose
- To ensure sample integrity
- To avoid hemolysis, contamination, or degradation
- To meet central lab quality standards
- To maintain consistency across sites globally
3 CRC Responsibilities in Sample Handling
3.1 Pre-Collection Preparation
CRC must ensure:
- Subject fasting requirements met (if applicable)
- Correct labels printed with:
- subject ID
- visit number
- date & time
- Correct vacutainers/tubes ready
- Lab manual reviewed before every visit
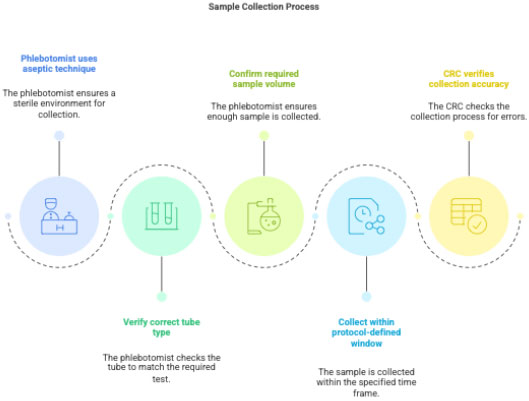
3.2 Sample Collection
Phlebotomist collects sample using aseptic technique.
CRC verifies:
- correct tube type (EDTA/SST/Heparin/etc.)
- correct volume
- correct time window
3.3 Sample Processing
As per laboratory manual:
- Centrifuge at required RPM and time
- Aliquot plasma/serum using sterile pipettes
- Label secondary aliquot tubes
- Document processing timepoints
CRC ensures centrifuge calibration is current.
3.4 Sample Storage
Depending on protocol:
- Store at 2–8°C, –20°C, or –80°C
- Ensure temperature logs maintained
- Use temperature-monitored freezers
- Ensure sample boxes organized and labeled
If temperature excursion occurs:
- Notify sponsor immediately
- Quarantine samples until further instructions
3.5 Sample Shipment
CRC coordinates:
- packaging with dry ice (if required)
- placing temperature data logger
- preparing chain-of-custody form
- booking courier pickup
- ensuring IATA-compliant labelling
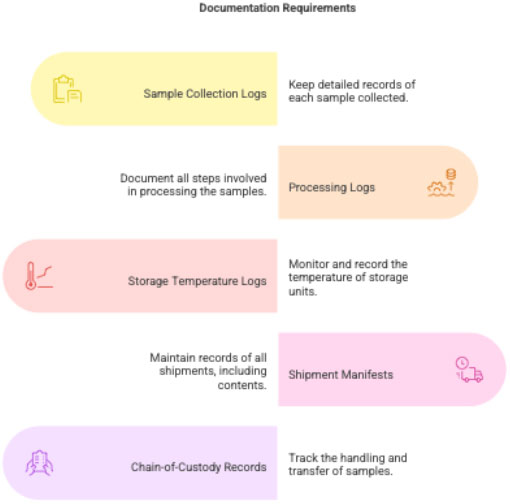
3.6 Documentation
- Sample collection log
- Processing log
- Storage temperature logs
- Shipment manifest
- Chain-of-custody records